Ventricular Rhythms
Premature Ventricular Complexes (PVC's)
- PVC's arise from an irritable focus within either ventricle.
- PVC's are premature - they occur earlier than the next expected sinus beat.
- PVC's are caused by enhanced automaticity or reentry.
Characteristics of PVC's
- Rate is usually within normal range but depends on underlying rhythm.
- Rhythm is essentially regular with premature beats.
- P wave is usually absent, or with retrograde conuction to the atria. May appear after the QRS.
- PRI - none with the PVC (because the ectopic beat originates in the ventricles).
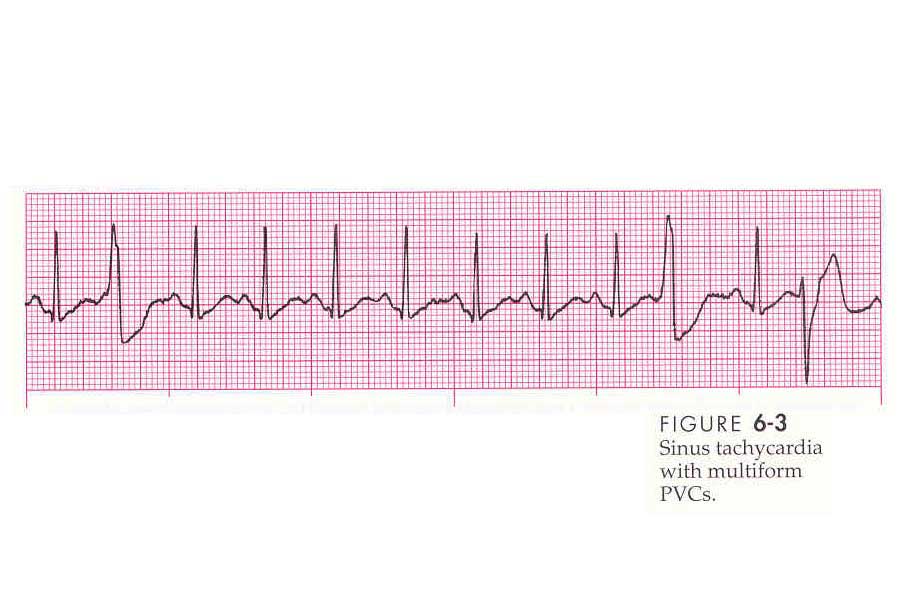
- QRS is greater than 0.12 seconds, wide, and bizarre, T wave frequently in opposite direction of the QRS complex. QRS is greater than 0.12 seconds because the PVC depolarizes the ventricles prematurely and in an abnormal manner.
Types of PVC's
- Pairs (couplets): 2 sequential PVC's
- Runs or bursts: 3 or more sequential PVC's (AKA Ventricular Tachycardia - VT)
- Bigeminy PVC's: Every other beat is a PVC.
- Trigeminy PVC's: Every thrid beat is a PVC.
- Quadrigeminy PVC's: Every fourth beat is a PVC.
Uniform and Multifocal PVC's
- Uniform PVC's: Look the same and originate from the same site.
- Multiformed: PVC's that appear different from one and other.
Common Causes of PVC's
- Hypoxia
- Stress, anxiety
- Exercise
- Digoxin toxicity
- CHF
- Acid-base imbalance
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Myocardial ischema
- Stimulants (ETOH, caffeine, tobacco)
- Meds
Clinical Significance
- PVC's can occur in healthy persons with apparently normal hearts, and for no apparent cause.
- PVC's may or may not produce palpable pulses. Patient's experiencing PVC's may be asymptomatic or c/o palpitations, a "racing heart," skipped beats, or chest/neck discomfort.
- If frequent s/s, decrease C.O. may be present.
Interventions
- Tx depends on cause, s/s, and on clinical situation. Most patients do not require tx with antidysrhythmic meds.
- Tx of PVC's seen in the setting of acute MI should be directed at ensuring adequate oxygenation , pain relief, rapid identification and correctino of hypoxia, heart failure, and electrolyte or acid-base abnormalities.

Ventricular Escape Beats/Rhythm
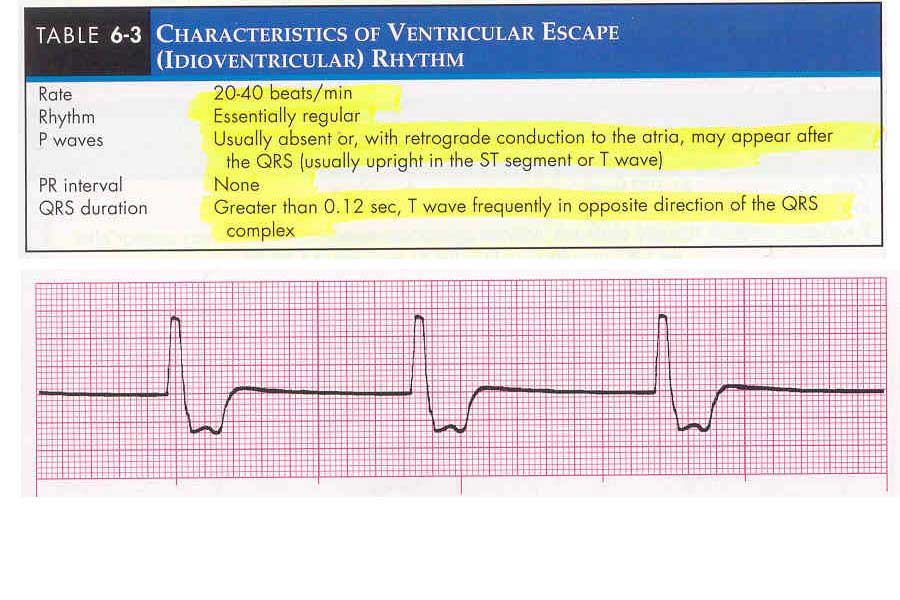
Characteristics of Ventricular Escape (Idioventricular) Rhythm
↑ Top of Page ↑